Image Filter
This page provides information on the Image Filter rollout in the V-Ray tab of the Render Settings.
Overview
While the Image Sampler determines the overall approach to pixel sampling to produce the color for each pixel, the image filter sharpens or blurs the transitions between adjacent pixel colors.
Image filtering is particularly important when textures in the rendering include very fine detail. For a still image rendering, the image filter can sharpen these details to make them more visible and prominent, or blur the pixels to reduce Moiré patterns and other unwanted artifacts. For an animated sequence, the choice of image filter can blur pixels to reduce "buzzing" and flickering of detailed textures during playback.
UI Path
||Render Setup window|| > V-Ray tab > Image filter rollout
Parameters
Image filter – Enables sub-pixel filtering of materials. When this option is disabled, an internal 1x1 pixel box filter is used. All image samplers support all 3ds Max's standard anti-aliasing filters except the Plate Match filter. Using filters increases rendering time.
Filter – Specifies the filter type. For more information, see The Anti-aliasing Filters example and The Anti-aliasing Filters and Moire Effects example below.
Avoid using filters with negative components (sharpening filters) like Catmull-Rom or Mitchell-Netravali when using the Progressive sampler. Doing so might dramatically increase render time as the sampler needs to take additional image samples to resolve the filter.
Size – Specifies the size of the image filter.
Example: Anti-aliasing Filters
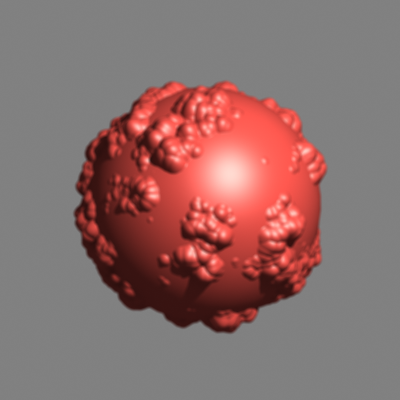
Here is an example briefly demonstrating the effect of different anti-aliasing filters on the final result.
Note that rendering with a particular filter is not the same as rendering without a filter and then blurring the image in a post-processing program like Adobe Photoshop. Filters are applied on a sub-pixel level, over the individual sub-pixel samples. Therefore, applying the filter at render time produces a much more accurate and subtle result than applying it as a post effect. V-Ray can use all standard 3ds Max filters (with the exception of the Plate match filter) and produces similar results to the scanline renderer.
The Bucket image sampler was used for the images below.
|
Filter |
Image |
Zoomed-in image |
Comments |
|
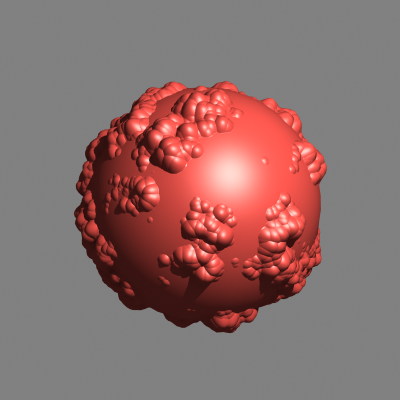
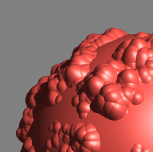
Filtering is off |
|
|
Applies an internal 1x1 pixel box filter. |
|
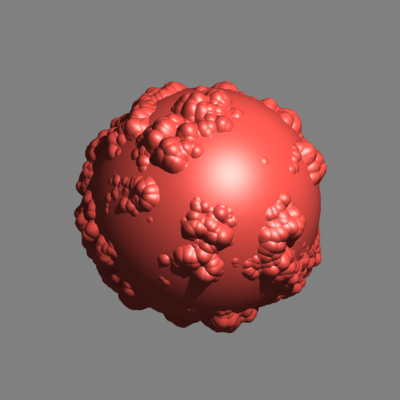
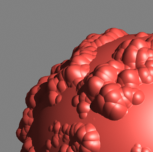
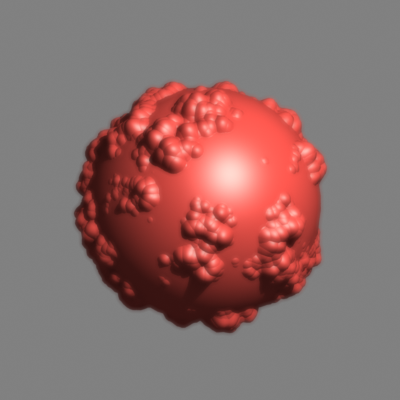
Area filter, size 1.5 (default setting) |
|
|
Slightly blurs the image, visually more pleasing than the box filter. |
|
Area filter, size 4.0 |
|
|
More blurring. |
|
Blend filter |
|
|
Combination of a sharp and a soft filter, kind of dreamy effect. |
|
Catmull-Rom |
|
|
Edge-enhancing filter, often used for architectural visualizations. Note that edge enhancing can produce "moire" effects on detailed geometry. |
|
Mitchell-Netravali |
|
|
Allows control between edge-enhancement and blurring. |
|
MItchell-Netravali, ringing=1.5 |
|
|
Strong edge-enhancement. |
|
Mitchell-Netravali, ringing=2.0 |
|
|
Even more edge enhancement; kind of cartoon-style effect. |
|
Soften |
|
|
Gaussian blur. |
Example: Anti-aliasing Filters and Moire Effects
This example demonstrates the effect anti-aliasing filters have on moire effects in your images. Sharpening filters (Mitchell-Netralavli, Catmull-Rom) may enhance moire effects, even if your image sampling rate is very high. Blurring filters (Area, Quadratic, Cubic) reduce moire effects.
Note that moire effects are not necessarily a result of poor image sampling. In general, moire effects appear simply because the image is discretized into square pixels. As such, moire effects are inherent to digital images. The effect can be reduced through the usage of different anti-aliasing filters, but is not completely avoidable.
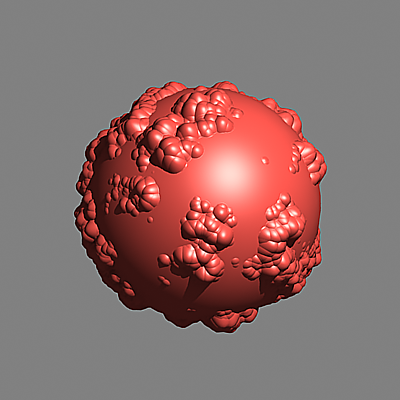
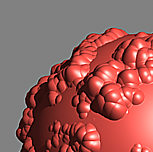
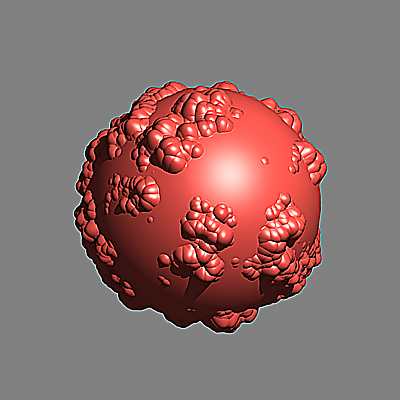
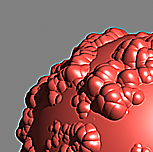
The scene is very simple: a sphere with a very fine checker map applied. The images were rendered with a very high sampling rate (15 subdivs, or 225 rays/pixel). This is enough to produce quite an accurate approximation to the pixel values. Note that the image looks quite different depending on the filter:
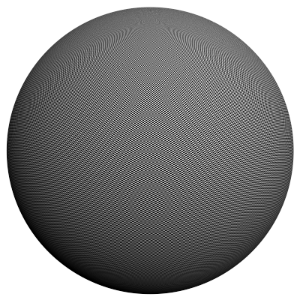
Image Filter off
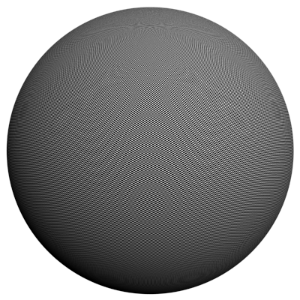
Area
size = 1.5

Area
size = 4.0
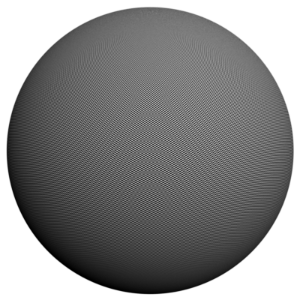
Quadratic
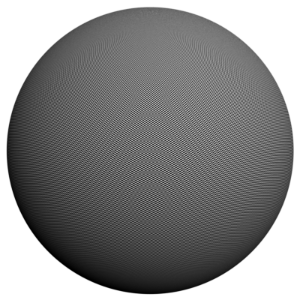
Sharp Quadratic
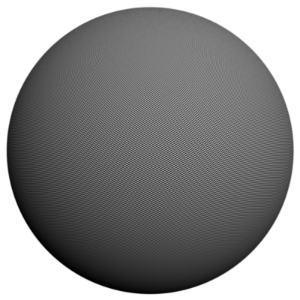
Cubic

Video

Soften
size = 6.0
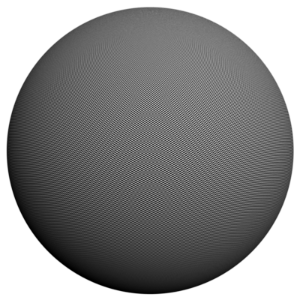
Cook Variable
size = 2.5

Blend
size = 8.0, blend = 0.3
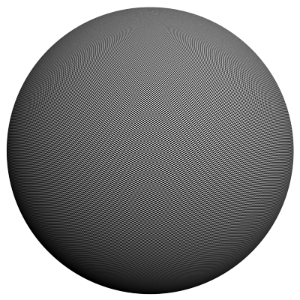
Blackman
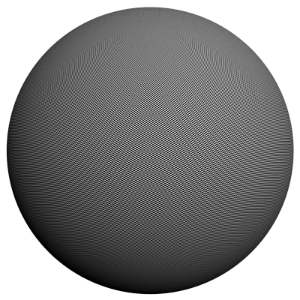
Mitchell-Netravali, blur = 0.333, ringing = 0.333
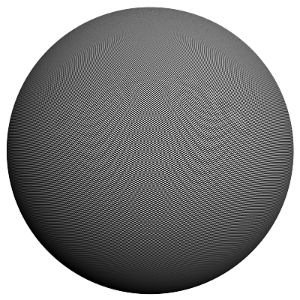
Catmull-Rom