GPU Light Cache
This page provides information on the Light Cache rollout in the V-Ray tab when V-Ray GPU is used as the production renderer.
Overview
The Light Cache rollout is available under the V-Ray tab when the GI engine is set to Light Cache and the render engine is V-Ray GPU. This rollout has three UI modes (Default, Advanced and Expert) available for change from the top-right corner of the rollout.
You can control various aspects of the Light Cache settings from this section. For more details on how the Light cache engine calculates GI, please see the Light Cache GI page under Indirect Illumination.
UI Path
||Render Setup window|| > V-Ray tab > Light Cache rollout
Parameters
Default UI Mode
Subdivs – Controls the quality of the Light Cache by determining how many paths are traced from the camera. The actual number of paths is the square of the subdivs (the default 1000 subdivs mean that 1,000,000 paths are traced from the camera). A value of 1000 is a good starting point, but higher values (2000 or 3000 or more) work better for more complex interior scenes and for reducing flickering in animations.
Sample Size – Controls the size of the individual Light Cache samples. Smaller values produce a more detailed lighting solution, but are noisier and take more RAM. Larger values produce less detail, but also take less RAM and may be faster to calculate.
Show calc. phase – Enabling this option shows the paths that are traced during the Light Cache calculation phase in the frame buffer. This does not affect the calculation of the Light Cache and only provides visual feedback to the user. This option is ignored when rendering to fields - in that case, the calculation phase is never displayed. This option does not work with distributed rendering.
Retrace – Enables retracing of GI near corners. This helps prevent light leaks and flickering. Normally, this should be enabled. The value specifies the extent to which GI near corners are retraced instead of being read from the Light Cache. A value of 0.0 disables retracing. A value of 2.0 is good for still images, and 8.0 is good for animations. Higher values result in more rays traced at render time.
Use camera path – This option is not available when rendering with V-Ray GPU.
Mode – Determines the rendering mode of the Light Cache:
Single frame – Computes a new Light Cache for each frame of an animation.
Fly-through – Computes a Light Cache for an entire fly-through animation, assuming that the camera position/orientation is the only thing that changes. The movement of the camera in the active time segment only is taken in consideration. Note that it may be better to set Scale to World for fly-through animations. The Light Cache for the entire animated sequence is computed only at the first rendered frame and is reused without changes for subsequent frames.
From file – The Light Cache is loaded from a file. The Light Cache file does not include the prefiltering of the Light Cache; prefiltering is performed after the Light Cache is loaded, so that you can adjust it without the need to recompute the Light Cache.
Progressive path tracing – The Light Cache algorithm is used to sample the final image progressively.
The Progressive path tracing mode is not supported by the V-Ray GPU engine, although it is visible in the UI. This option works best with Primary and Secondary GI engine set to Light Cache, which is not supported in V-Ray GPU.
File – Specifies the file name to load the Light Cache from, when the Mode is set to From file.
Save – Saves the Light Cache that remains in memory after the rendering to a file on disk for later reuse. Note that the Don't delete option must be enabled for this to work. Otherwise, the Light Cache is deleted as soon as rendering is complete, and it is not be possible to save it.
Advanced UI Mode
Scale – Determines the units of the Sample size.
Screen – The units are fractions of the final image (a value of 1.0 means the samples are as large as the whole image). Samples that are closer to the camera are smaller, and samples that are far away are larger. Note that the units do not depend on the image resolution. This value is best suited for stills or animations where the Light Cache needs to be computed at each frame.
World – The samples are with fixed size in world units everywhere. This can affect the quality of the samples - samples that are close to the camera are sampled more often and appear smoother, while samples that are far away are noisier. This value might work better for fly-through animations, since it forces constant sample density everywhere.
Pre-filter – When enabled, the samples in the Light Cache are filtered before rendering. Note that this is different from the normal Light Cache filtering controlled by the Filter parameter, which happens during rendering. Prefiltering is performed by examining each sample in turn, and modifying it so that it represents the average of the given number of nearby samples. More prefilter samples mean a blurrier and less noisy Light Cache. Prefiltering is computed only once after a new Light Cache is computed or loaded from disk.
Use for glossy rays – When enabled, the Light Cache is used to compute lighting for glossy rays as well, in addition to normal GI rays. This can speed up rendering of scenes with glossy reflections quite a lot. When using this option, it is recommended to also enable the Retrace option, which prevents the Light Cache from being visible in very glossy surfaces.
Filter – Determines the type of render-time filter for the Light Cache. The filter determines how irradiance is interpolated from the samples in the Light Cache.
None – No filtering is performed. The nearest sample to the shaded point is taken as the irradiance value. This is the fastest option, but it might produce artifacts near corners if the Light Cache is noisy. You can use the Pre-filter setting to decrease the noise. This option works best for testing purposes.
Nearest – Looks up the nearest samples to the shading point and averages their value. This filter adapts to the sample density of the Light Cache and is computed for a nearly constant time. The Interp. samples parameter determines how many of the nearest samples to look up from the Light Cache.
Fixed – Looks up and averages all samples from the Light Cache that fall within a certain distance from the shaded point. The size of the filter is determined by the Filter size parameter. Larger values blur the Light Cache and smooth out noise. Typical values for the Filter size are 2-6 times larger than the Sample size. Note that Filter size uses the same scale as the Sample size, and that the units used depend on the Scale parameter.
Store direct light – When enabled, the Light Cache also stores and interpolate direct light. This can be useful for scenes with many lights, since direct lighting is computed from the Light Cache instead of sampling each and every light. Note that only the diffuse illumination produced by the scene lights is stored. If you want to use the Light Cache directly for approximating the GI while keeping the direct lighting sharp, disable this option.
Interp. samples – Specifies the number of Light Cache samples to blend together when the Filter type is set to Nearest. Larger values take longer to compute during the rendering phase.
Don't delete – When enabled (the default), the Light Cache remains in memory after the rendering. Disable this option to automatically delete the Light Cache (and thus save memory).
Auto save – When enabled, the Light Cache is automatically written to the specified file. Note that the Light Cache is written as soon as it is calculated, rather than at the actual end of the rendering.
To save a separate Light Cache file for each frame of an animation, append %04d suffix to the name of the file.
Switch to saved cache – When enabled, after the rendering is complete, the Light Cache Mode is automatically set to From file and the name of the auto-saved Light Cache file is copied to the File parameter.
Expert UI Mode
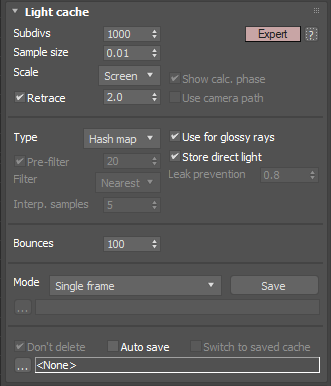
Type – Specifies which method to use to calculate the Light cache.
Hash map –
This is the default light cache type for new scenes. It is a
new light cache implementation that is simpler and produces less flickering in animations. Old light cache maps will not work with the new Hash method.
KD tree –
The original light cache implementation.
Leak prevention – Additional calculations are performed to prevent light leaks and reduce flickering with the Light Cache. A value of 0.0 disables the leak prevention. The default value of 0.8 should be adequate for most cases.
Bounces – Controls the maximum number of secondary bounces that a ray of light may make. Note that this value is an upper limit.